Loading...
|
- Home
-
Products
- Computerised Radiography
- Covid-19
- Hand hygiene products
- In-Vitro Diagnostics
- Newborn Screening
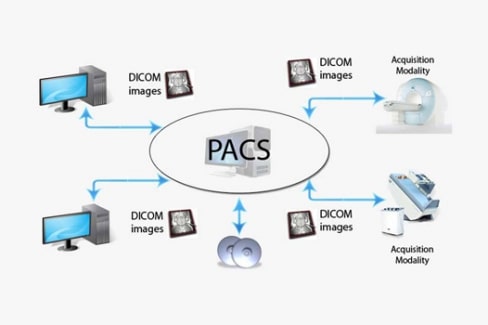
- PACS Solutions
- Point of Care Test
- Radiology Printing Solutions
- Surface Disinfectants
- Veterinary Radiography
- Mammography
- Radiography & C-Arm Systems
- HPLC
- Ultrasound
- Radiation Protection
- ICU Solutions
- Clinical Chemistry
- Hematology
- Immunology
- Infectious Disease
- Gastroenterology
- Radiology Accessories
- Fluoroscopy